DERMS Implementation Solutions
As the grid of the future takes shape, utilities are turning to distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS) to meet the pressing challenge of effectively integrating and utilizing distributed energy resources (DERs). The fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources and the complexity of managing a diverse array of DERs underscore the need for strategic implementation of high-performant DERMS solutions.
DERMS deliver the capabilities utilities need to manage DERs in real time, enabling continuous communication, control, and data flows across solar panels, batteries, and other behind-the-meter devices. Understanding how DERMS work is crucial, as they integrate and manage DERs to optimize energy consumption and generation. Energy storage systems, such as batteries and electric vehicles, play a vital role in enhancing grid resilience and reliability. Forward-looking utilities are leveraging DERMS software to achieve a truly optimized power grid, improved efficiency and resilience, and enhanced ability to respond to power emergencies. DERMS also help manage energy production from renewable sources by forecasting energy production and demand, ensuring that the right amount of power is dispatched to meet electricity needs.
watts of power to be produced by DERs by 2025
(source about how DER implementation to grow to 380 gigawatts by 2025)
dollars = the size of the global DERMS market by 2030
(source about how global DERMS market will reach $1.86 billion by 2030)
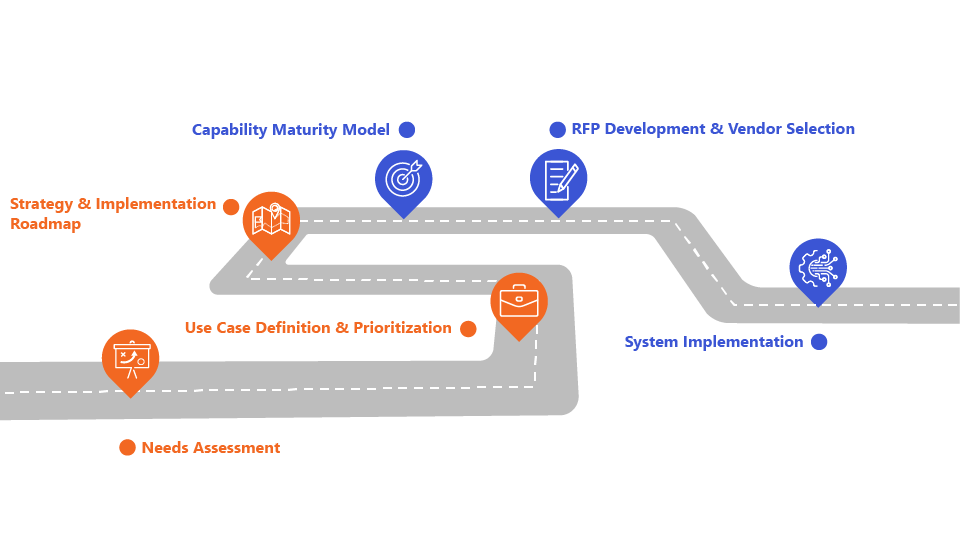
Our Approach to DERMS solutions
Logic20/20 helps utilities maximize ROI on their DERMS investments by focusing on key areas:
WEBINAR
Harnessing the power of DERMS: enhancing the grid’s flexibility and reliability
WHITE PAPER
Planning for net-zero utilities: Integrating renewables and DERs
DERMS use cases
A key part of a utilities distributed energy management system strategic roadmap and planning includes prioritizing top use cases and weighing an asset vs. grid centric approach. By focusing on the most impactful use cases, utilities can provide a comprehensive, real-time overview of distributed energy resources (DERs) and their effects on the electrical grid. Additionally, the evolving energy landscape presents a diverse range of energy resources, adding complexities that utilities must navigate to integrate various energy sources effectively. By focusing on the most impactful use cases, utilities can address critical challenges such as load balancing, peak demand management, and renewable energy integration more effectively.
This strategic approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also maximizes the return on investment in a DERMS software platform that enhances the integration and optimization of various distributed energy resources.
DER Visibility
System operator visibility to DER telemetry
Dynamic Operating Envelope
Adaptive gen and load limits for optimal constraint management
Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
Aggregation of DERs – storage, solar, & DR assets
Vehicle-to-Grid Integration
Bidirectional power flow (i.e. EV batteries & the grid) and aggregation & managed charging
DER Forecasting
Days/Hours ahead forecasting, and net load & DR available flexible capacity
Key Considerations for Choosing DERMS Vendors
Alignment of Utility Need with Vendor Capability
Evaluate how well the vendor’s offerings align with the electric utilities’ specific business objectives and use cases particularly in managing distributed energy resources (DERs) through systems like DERMS. Ensure the DERMS solution offers a path to achieving quicker ROIs through its capabilities and deployment efficiency.
Scalability and Customization
Determine how well the vendor can accommodate future growth and customization needs of the utility, especially for functionalities that may not currently exist. A robust network model is crucial in this context, as it enhances reliability and performance in energy management systems, facilitating utilities in managing and regulating Distributed Energy Resources (DERs).
Peer Utility Experience
Consider the experiences of peer utilities who have implemented the vendor’s DERMS solution to gauge its effectiveness and reliability.
Partnership Landscape
Explore the vendor’s recent partnerships, like Schneider Electric’s collaboration with Uplight/AutoGrid, to understand how the alliances enhance the DERMS capabilities.
Customer Base and Cost Implications
Assess the vendor’s customer base size, as a larger base can potentially lower costs through shared development and deployment expenses.
Integration Strategy
Assess the vendor’s capability to integrate Grid Edge DERMS and Utility DERMS seamlessly, ensuring comprehensive management of DERs. Evaluate how the DERMS software enhances grid operations by improving the control, coordination, and optimization of distributed energy resources (DERs). This includes enhancing grid security and integrating renewable energy sources, thereby facilitating more efficient and effective management within the energy network.
Implementation Experience
Evaluate the vendor’s track record in implementing DERMS solutions, considering both the cost of initial implementation and ongoing feature development.
Out-of-Box Capability
Gauge the readiness of the DERMS solution out of the box, minimizing the need for extensive modifications or updates to meet operational requirements efficiently.
Outcomes
Enhanced grid stability
Mitigate the variability of renewable energy sources by managing the flow of power from DERs on the DERMS platform, ensuring grid stability and maintaining a reliable and efficient energy infrastructure.
Improved efficiency
Optimize the dispatch of DERs to reduce the need for expensive peak power generation and increase overall grid efficiency. Effective coordination of these technologies can lead to significant cost savings while also improving grid security.
Increased resilience
Enhance grid resilience against outages by quickly redistributing energy resources where needed, thereby improving grid reliability.
Demand response management
Support demand response programs by controlling DERs to reduce load during peak demand times.
Data-driven insights
Gain insights into energy usage patterns, system vulnerabilities, and opportunities for further optimization.
Case study
Powering change: implementing DERMS for enhanced energy resource management
Learn how we’re helping a major West Coast utility move towards an enterprise DERMS solution that provides seamless access to DER capacity information and enables an integrated approach to grid management.

DERMS Insights

DERMS: Essential strategies for implementation
4 starting steps to help ensure optimized integration of DERMS with existing data platforms

Preparing utilities: DER and renewable energy regulations
How utilities are preparing for new regulations related to DERs by building robust compliance systems

AI’s role in adapting DER aggregators
AI-driven tools and technologies that can help DER aggregators adapt to their role in shaping the grid of the future
What are your challenges? Let’s talk through the solutions.