Wildfire Mitigation Planning
Driving wildfire mitigation planning with predictive risk management
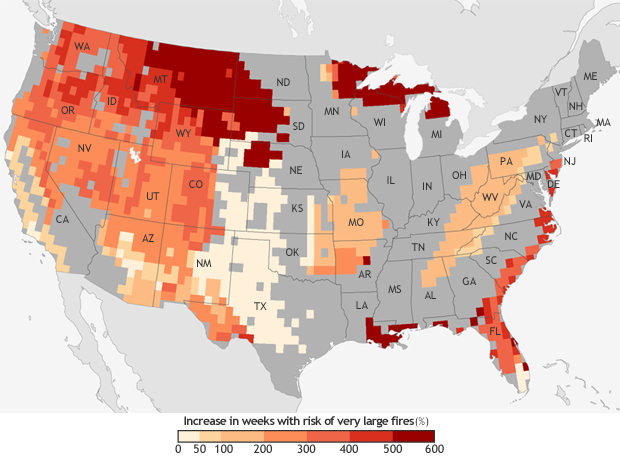
According to a recent Congressional report, the annual economic burden of wildfires reaches as high as $893 billion. By mid-century, the risk of wildfires could increase six-fold in some areas (see map).
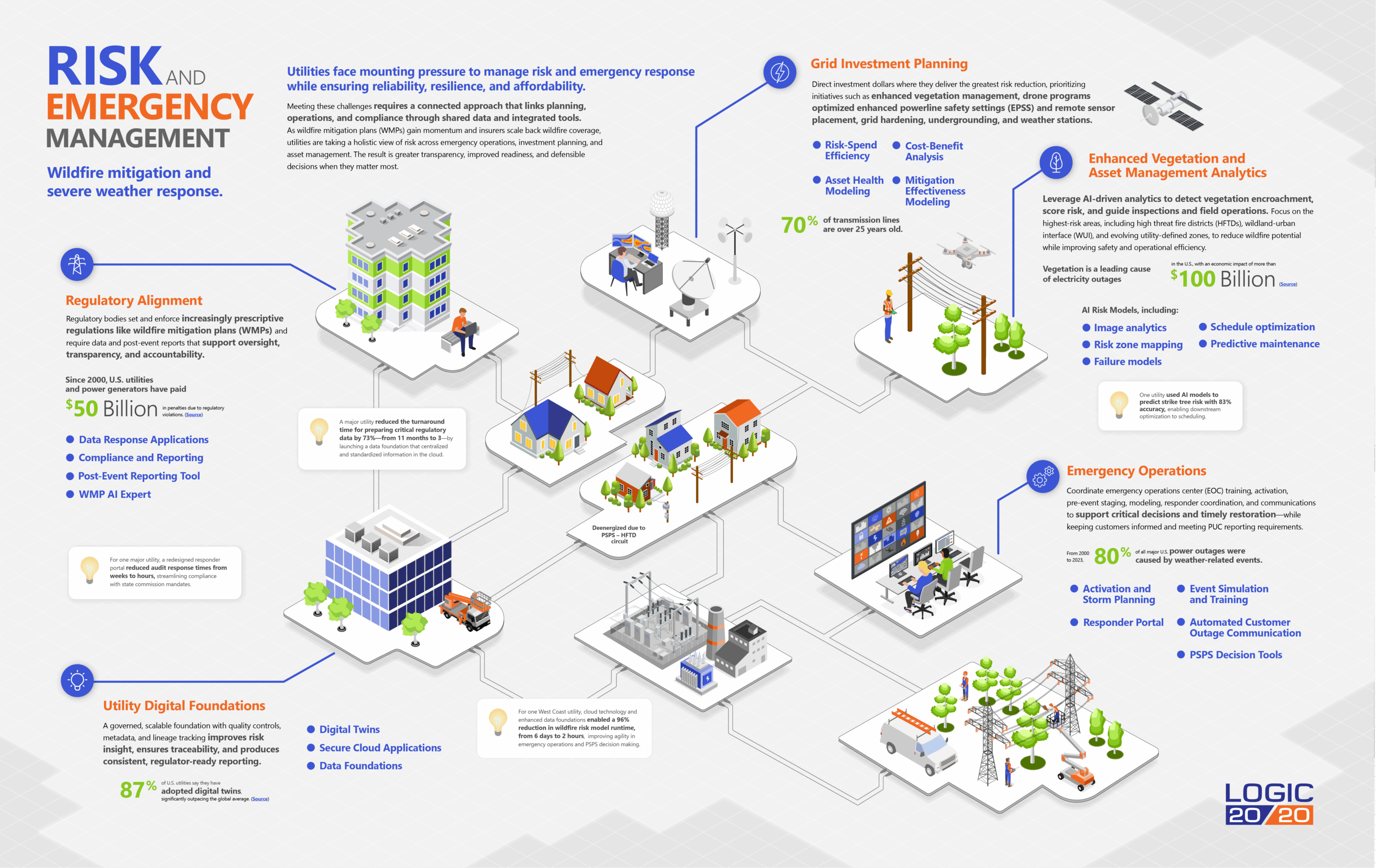
As wildfires increase in frequency and in cost to the U.S. economy, utilities are under increasing pressure to escalate their mitigation efforts—both from regulatory bodies and from concerned stakeholders. Establishing a clear action plan is crucial for effective wildfire mitigation. This includes taking responsible actions by individual property owners and fostering collective actions within communities.
Logic20/20 taps into the power of AI and machine learning to help utility providers assess wildfire risks, fine-tune their response plans to reduce risk, and meet compliance obligations to report on their wildfire mitigation plans (WMPs).
Risk intelligence: Aligning on goals and requirements for resilience
Realizing positive ROI from wildfire mitigation initiatives and programs requires a comprehensive approach to align on the goals and requirements of risk intelligence capabilities:
STRATEGY
- Risk assessment & wildfire mitigation strategy
- Situational awareness & forecasting from wildfire risk modeling
GRID
- Grid design, inspections & maintenance
- Grid operations & protocols
EXECUTION
- Vegetation management & inspections
- Asset health monitoring & inspections
- Emergency preparedness & community engagement
- Modern risk modeling tools and techniques
Wildfire mitigation plan outcomes
Improved reliability – SAIDI and SAIFI
Reduced risk of catastrophic wildfire
Improved ROI of strategic grid investment and hardening
Increased preparedness to meet new regulatory requirements
Data response applications
Automate responses to regulators’ data requests through governed workflows and reusable templates, with data lineage supporting traceability and audit readiness.
Compliance & reporting
Enhance compliance tracking and reporting with automated, data-driven systems aligned to regulatory requirements. Consolidate evidence and metrics for filings, audits, and post-event reports with standardized datasets and clear audit trails.
Post-Event Reporting Tool
The post-event reporting tool automates EOC report-backs, generating regulator-ready records for commissions like the PUC or FERC.
WMP AI Expert
AI-driven authoring helps utilities generate wildfire mitigation plans (WMPs) aligned to local requirements, risk models, and program evidence, producing consistent, regulator-ready documentation.
Digital Twin
High-fidelity grid and asset digital twins combine geospatial, asset health, and weather data to improve risk decision making.
Secure Cloud Applications
Secure, scalable cloud-based applications deliver role-based insights and controlled access across utility teams.
Data Foundations
A governed, scalable foundation with quality controls, metadata, and lineage tracking improves risk insight, ensures traceability, and produces consistent, regulator-ready reporting.
Responder Portal
Provide responders with secure access to infrastructure maps and safety information to support situational awareness, emergency response, training and cross-agency coordination.
Activation and storm planning
Evaluate conditions, model thresholds, and map asset risk to inform PSPS decisions. Built-in reporting ensure actions are defensible and customer impacts are clearly assessed.
Automated Customer Outage Communication
Automated SMS, email, voice, and portal alerts keep customers informed of outages, PSPS, and restoration to meet regulatory requirements while improving transparency.
PSPS Decision Tool
Evaluate conditions, model thresholds, and map asset risk to inform PSPS decisions based on risk and current conditions. Built-in reporting ensure actions are defensible and customer impacts are clearly assessed.
Risk modeling solutions
Leverage Risk-Spend Efficiency and Cost-Benefit Analysis to prioritize investments in risk reduction for wildfire mitigation and increased reliability
Optimize inspection and maintenance processes
Define high risk zones for enhanced vegetation and asset management and optimize inspection scheduling to reduce truck rolls and risk.
WEBINAR
Building a scalable wildfire mitigation program with a comprehensive approach to risk analytics
WHITE PAPER
Unified risk modeling for utility resilience
It all starts with predictive risk modeling
Logic20/20 provides an enterprise risk management framework to guide your utility in operationalizing predictive insights to address wildfire risks. The same principles apply to wildfire risk mitigation as to other risk modeling.
Identify
risk using process and tools.
Analyze
with data insights and expert input.
Evaluate
mitigations, efficacy, and timeframes.
Prioritize
risks and mitigations.
Respond
to risk.
Monitor
remaining or residual risk.
Wildfire Mitigation Planner
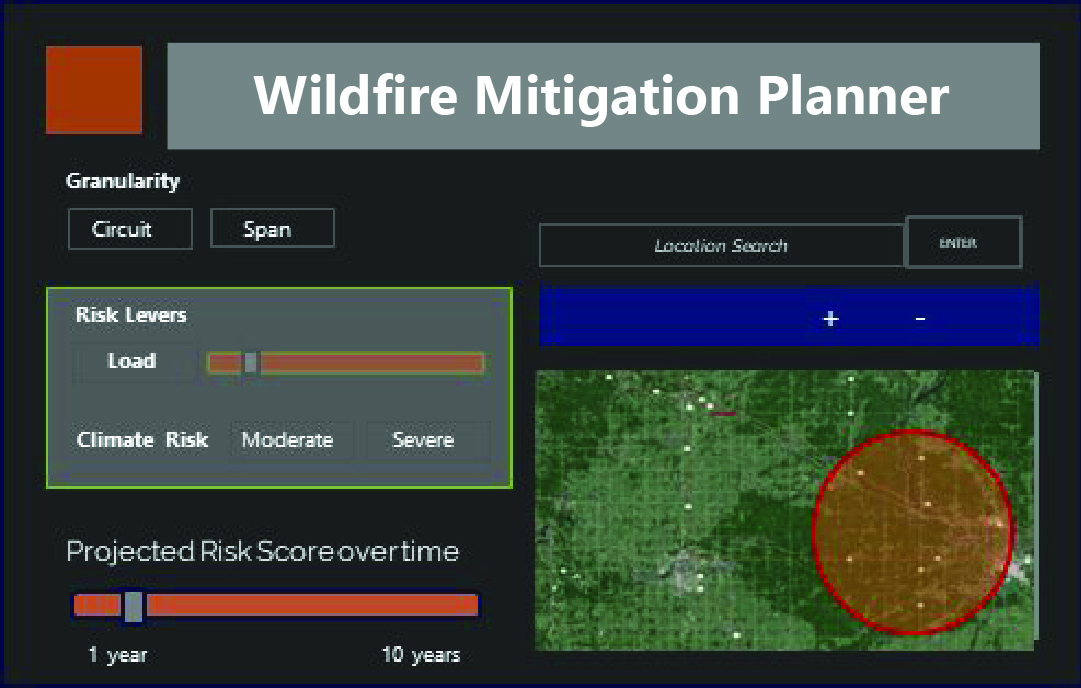
Data integration
- Vegetation
- Climate projections
- Customer systems
- Weather
- Asset information
- Fire simulation
Investment outcomes
- ROI: Investment dollars meaningfully reduce wildfire risk
- Reliability: Fewer unplanned outages and failures
- Safer communities: Lives and communities protected with wildfire risk reduction
Mitigation strategies
Defensible space
Defensible space is a critical component of wildfire mitigation. It refers to the area around a home or building that is cleared of combustible materials, such as dead leaves, branches, and debris. Creating defensible space can help prevent embers from igniting a fire and reduce the risk of damage to homes and buildings.
To create defensible space, homeowners can take several steps:
- Clear dead leaves and debris from gutters and roofs/
- Trim trees and shrubs to maintain a safe distance from homes and buildings/
- Remove combustible materials, such as dead branches and needles, from the area around homes and buildings/
- Use fire-resistant materials for roofing and siding/
- Create a safe zone around homes and buildings by clearing flammable materials/
Landscape fuel treatment
To implement landscape fuel treatments, landowners and managers can take several steps:
- Assess the landscape to identify areas at high risk of wildfires.
- Develop a comprehensive plan to modify the landscape and reduce fuels.
- Implement fuel treatments, such as thinning and prescribed burning.
- Monitor and maintain the landscape to ensure that fuels are kept at a safe level.
Public Safety Power Shutoff (PSPS) dashboard
Extreme weather preparedness
Extreme weather events, such as droughts and heatwaves, can increase the risk of wildfires. Communities can take steps to prepare for extreme weather events and reduce the risk of wildfires.
To prepare for extreme weather events, communities can take several steps:
- Develop a comprehensive emergency plan that includes procedures for responding to wildfires.
- Conduct regular maintenance on equipment and infrastructure to ensure that it is in good working condition.
- Provide education and outreach to residents on the risks of wildfires and the importance of preparedness.
- Develop a plan for evacuating residents in the event of a wildfire.
- Identify areas at high risk of wildfires and take steps to mitigate those risks.
Wildfire mitigation planning insights

Webinar: Building a scalable wildfire mitigation program with a comprehensive approach to risk analytics
Wildfire mitigation is becoming a national concern as temperatures across the country rise, weather patterns change, and demand on the grid intensifies.

Building a risk-aware utility with wildfire risk modeling
A four-phase approach to wildfire mitigation that helps utilities assess, prioritize, and reduce wildfire risks effectively. Home site visits are a best practice for engaging property owners in risk-reduction activities.

Case study: Mitigating wildfire risk with computer vision-aided asset management and machine learning
Use computer vision to reduce remote aerial image inspection time and cost, with the goal of finding and replacing damaged equipment before it fails and sparks a wildfire.
What are your challenges? Let’s talk through the solutions.