7-minute read
Quick summary: By leveraging AMI data, utilities are uncovering new possibilities for enhancing efficiency, reliability, and customer service, marking a transformative shift in utility management and customer engagement.
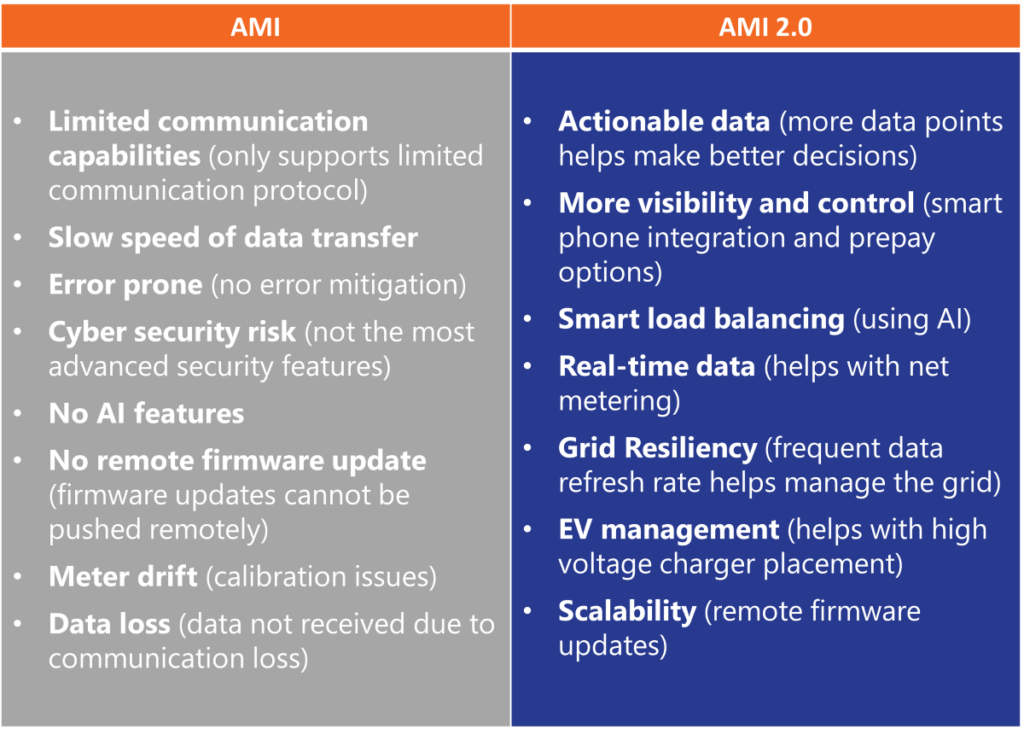
As the utility landscape continues its rapid evolution, the shift from traditional metering to advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) marks a pivotal change, ushering in a new era of reliability, efficiency, and customer engagement. The transition to AMI, and the subsequent emergence of AMI 2.0, represents more than a technological leap; it signifies a profound transformation in utility operations and customer interactions.
With AMI systems collecting vast volumes and varieties of data—from detailed consumption patterns to voltage profiles to detection of EV chargers and rooftop solar —the potential to revolutionize utility management through data analytics is immense. This wealth of information, when analyzed effectively, can transform into actionable insights, empowering utilities not only to meet current demands but also to design future-ready infrastructures.
Article continues below.
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI)
Explore how advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) solutions help utilities drive efficiency, improve grid reliability, and deliver better customer experiences.

The leap to AMI 2.0
The evolution from AMI to AMI 2.0 marks a paradigm shift in how metering data is collected, analyzed, and acted upon. This leap is not merely an upgrade but a comprehensive enhancement that redefines the potential of utility data management. While AMI laid the groundwork for smart metering and data collection, AMI 2.0 takes this foundation and elevates it, enabling a more dynamic, responsive, and efficient utility infrastructure.

White paper: Unlocking the ROI of AMI 2.0
A strategic approach to prioritizing use cases for maximum impact
We will never sell your data. View our privacy policy here.
Harnessing the power of AMI data
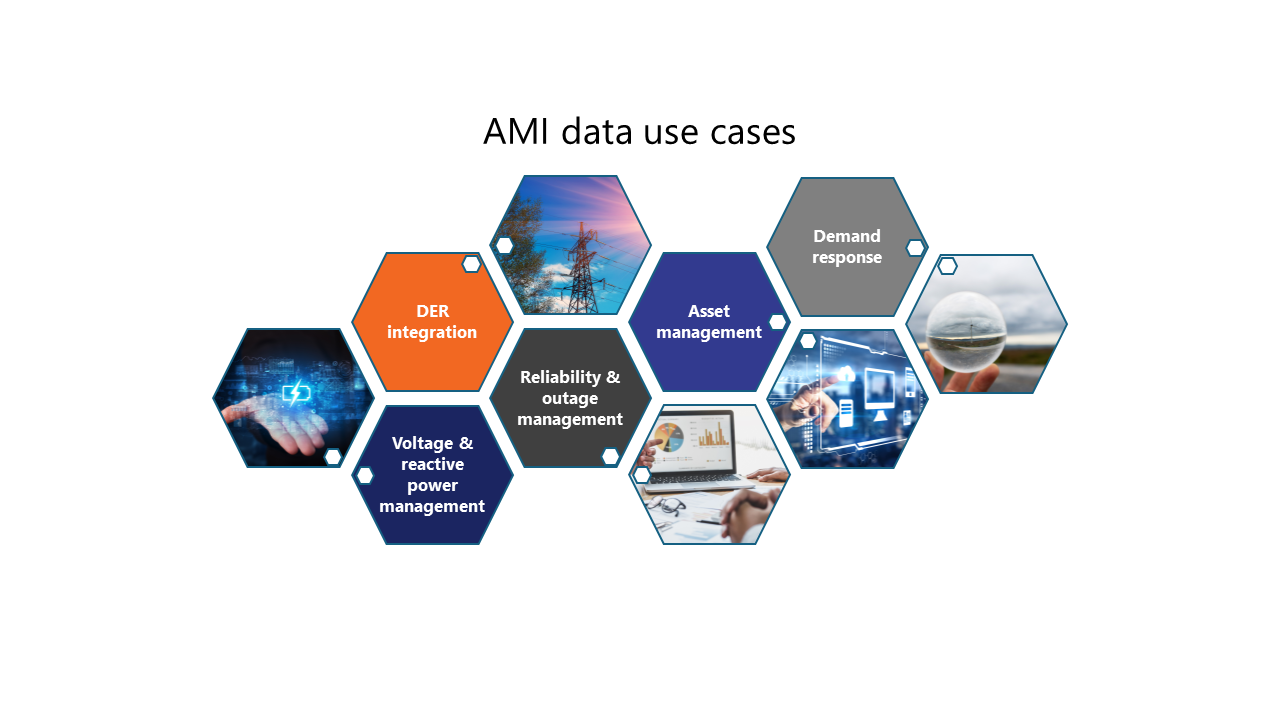
AMI’s volume and variety of data—delivered at a rapid velocity—provide utilities with raw materials for building insights that can drive dramatic improvements in grid stability, distributed energy resource (DER) integration, demand response, and more.
Managing assets proactively
- Monitor utility equipment continuously to anticipate and prevent failures
- Extend equipment lifespan and performance through transformer monitoring and load management.
- Identify and address high-impedance signals to prevent potential disruptions.
Enhancing grid reliability and managing outages
- Accelerate recovery with Fault Location, Isolation, and Service Restoration (FLISR).
- Keep customers updated through sophisticated outage monitoring and notification systems.
- Streamline restoration efforts with optimized dispatch strategies.
- Ensure effective response plans with advanced analysis of customer data.
- Monitor utility equipment continuously to anticipate and prevent failures.
Optimizing voltage and power quality
- Achieve optimal power delivery through integrated voltage and volt-ampere reactive (VAR) controls (IVVC).
- Stabilize the grid with automated voltage adjustments.
- Implement conservation voltage reduction (CVR) to reduce energy use without compromising service.
- Balance network load in real time for equitable power distribution.
- Enhance system efficiency and minimize losses with automated power factor corrections.
Supporting demand response programs
- Promote energy conservation during off-peak hours with time-based rates.
- Manage peak load effectively with direct load control measures.
- Implement strategies for reducing peak demand, alleviating grid stress.
- Protect revenue by ensuring accurate billing and mitigating loss.
- Achieve optimal power delivery through integrated voltage and volt-ampere reactive (VAR) controls (IVVC).
Integrating distributed energy resources (DERs)
- Streamline the management and dispatch of DERs for improved grid support.
- Efficiently utilize customer-sited energy storage.
- Coordinate EV charging to manage peak load without overloading the grid.
- Facilitate long-term planning with integrated resource strategies.
- Implement net metering and billing to fairly compensate for energy contributions from customers.
Real-world impact of data-driven insights
So, what do all these AMI data use cases mean in terms of addressing a utility’s day-to-day challenges? Here are two powerful examples.
Navigating renewable integration
The growing penetration of renewable energy sources (e.g. rooftop solar) and energy-intensive devices (e.g. electric vehicles) is causing seismic shifts in both the supply and demand sides of the grid. To complicate matters further, EVs can act as both consumers and suppliers of electricity if owners choose to participate in vehicle-to-grid (V2G) programs. As a result, many utilities are encountering difficulties in balancing grid loads on a day-to-day basis.
Utility providers can combine AMI data with weather forecasts, EV ownership figures, and other sources to improve predictions of energy supply and demand. For example, on a sunny day, it’s likely that rooftop solar owners will be supplying energy back to the grid. By applying advanced analytics to the sources available to them—including AMI feeds—utilities can rebalance the load and better manage grid resources in real or near-real time.
Responding to extreme weather events
Extreme weather conditions such as heat waves, storms, and hard freezes can generate grid stability issues due to increased demand for electricity (e.g. air conditioning during heatwaves) or damage to infrastructure (e.g. fallen power lines during storms). AMI can provide the data utilities need to maintain a stable grid during extreme weather events in several applications:
- Load forecasting and demand response: By analyzing patterns of consumption during previous extreme weather events, utilities can predict peak demand periods and plan appropriate responses. AMI data also helps identify high-demand areas, allowing utilities to target specific neighborhoods for demand response programs.
- Asset management and predictive maintenance: AMI data provides real-time insights into the health of distribution transformers, substations, and other grid assets, enabling utilities to identify damaged infrastructure promptly. Predictive maintenance based on AMI data helps utilities schedule maintenance activities efficiently, reducing the risk of damage in severe weather conditions.
- Voltage regulation and grid stability: Extreme weather events can cause voltage fluctuations, and AMI data allows utilities to monitor voltage levels at individual customer premises. By fine-tuning voltage regulation using AMI data, utilities can prevent overloading and voltage sags, ensuring uninterrupted service.
Unlock the potential of AMI data
In a world where data has been called “the new oil,” utilities equipped with AMI are sitting atop an untapped reservoir. The journey from data collection to actionable intelligence is marked by a series of critical tasks, each designed to ensure that utilities not only harness the power of AMI data, but do so in a manner that is scalable, secure, and seamlessly integrated into their existing operations.
Evaluating data infrastructure
Begin by assessing your utility’s capabilities in capturing, storing, and processing data. This includes understanding your current infrastructure’s limitations and identifying improvements needed to handle the influx of data from AMI systems. Consider implementing AI and machine learning algorithms to automatically clean, process, and analyze AMI data, identifying patterns and predictions that human analysis might miss.
Building a scalable analytics platform
The foundation of effective AMI data utilization is a robust analytics platform capable of scaling with your utility’s growing data needs. This platform should be designed with flexibility in mind, allowing for the integration of advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning to glean data-driven insights. Leverage machine learning to refine data models over time, improving the accuracy of predictions related to consumption patterns, grid stability, and anomaly detection.
Choosing the right vendor
Evaluate vendors not just on their technology offerings but also on their experience in the utility sector, their understanding of the regulatory landscape, and their ability to provide solutions that can scale with your utility’s growing needs.
Implementing robust data management strategies
AMI delivers data to utilities at unprecedented scale and speed. Ensuring data accuracy, timeliness, and relevance requires strong data management practices, including clear protocols for data quality, storage, and governance.
Addressing security and integration challenges
Utilities must navigate the security and privacy implications of handling vast amounts of consumer data. Achieving this goal requires implementing rigorous cybersecurity measures and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. Additionally, AMI data systems must integrate smoothly with the utility’s existing IT/OT ecosystem, which requires careful planning and execution.
By methodically addressing these areas, utilities can transform their AMI data from a passive resource into a dynamic tool for operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Charting the course for utility innovation
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in utility management, the journey from traditional metering to the advanced capabilities offered by AMI and AMI 2.0 marks a significant shift towards a more dynamic, efficient, and customer-centric operational model. AMI systems and their ability to gather vast arrays of data present an unparalleled opportunity to reshape the landscape of utility management. Analyzing this data effectively can yield actionable insights, empowering utilities to meet the demands of today and architect the infrastructure of tomorrow.
The path forward with AMI data is not just about leveraging new technology for the sake of innovation; it’s about strategically enhancing every facet of utility operations—from voltage management and outage response to asset maintenance and customer engagement. By embracing AMI 2.0, utilities can unlock the full potential of this data to drive efficiencies, bolster grid resiliency, and pave the way for a sustainable energy future.

Powering a sustainable tomorrow
- Smart automation
- DERMS implementation
- Analytics & predictive insights
- Cloud optimization


