Utility Risk Management
Proactively managing risk across the utility landscape
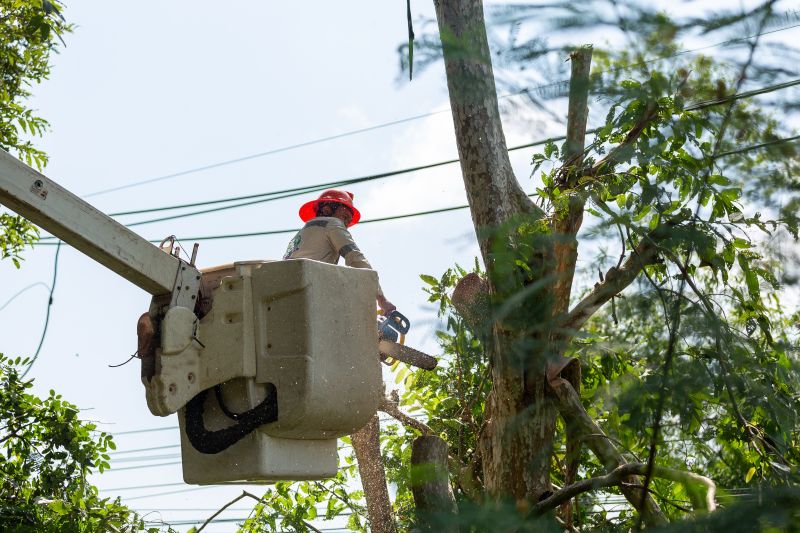
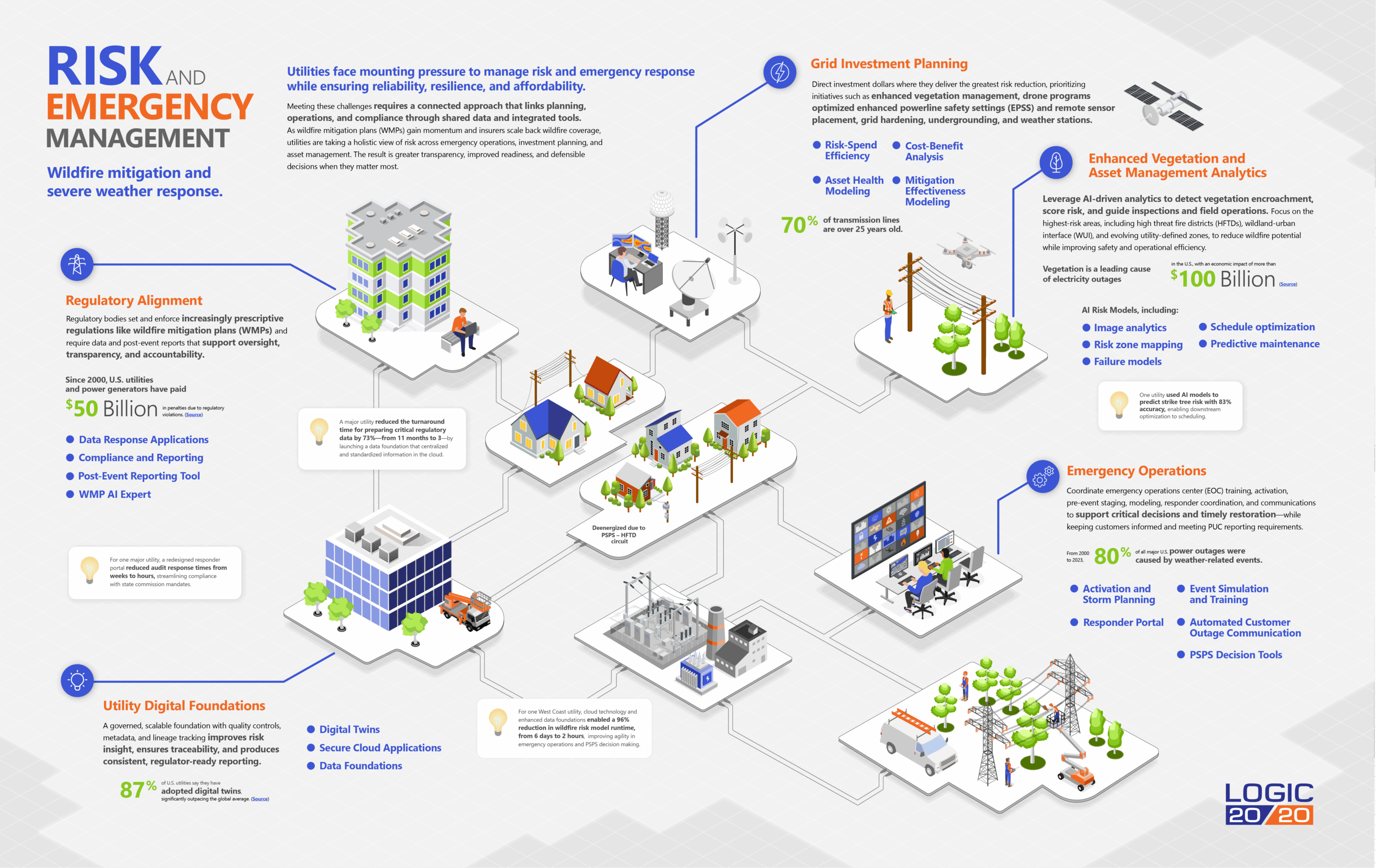
Utilities face increasing pressure from environmental threats, regulatory requirements, and aging infrastructure—challenges that create risk across transmission, distribution, vegetation management, and emergency operations. Addressing these risks requires more than a single system or process; it calls for a coordinated suite of solutions that work together to improve awareness, prioritize actions, and strengthen resilience.
At the center of Logic20/20’s approach is the Utility Risk Framework—a scalable foundation that connects asset, environmental, and operational data to drive informed decision making across the enterprise. Surrounding it is a set of targeted solutions, each designed to support specific functions while contributing to a unified risk posture. The result: a transparent, agile, and data-driven operation equipped to respond to today’s evolving utility landscape.

Data response applications
Automate responses to regulators’ data requests through governed workflows and reusable templates, with data lineage supporting traceability and audit readiness.
Compliance & reporting
Enhance compliance tracking and reporting with automated, data-driven systems aligned to regulatory requirements. Consolidate evidence and metrics for filings, audits, and post-event reports with standardized datasets and clear audit trails.
Post-Event Reporting Tool
The post-event reporting tool automates EOC report-backs, generating regulator-ready records for commissions like the PUC or FERC.
WMP AI Expert
AI-driven authoring helps utilities generate wildfire mitigation plans (WMPs) aligned to local requirements, risk models, and program evidence, producing consistent, regulator-ready documentation.
Digital Twin
High-fidelity grid and asset digital twins combine geospatial, asset health, and weather data to improve risk decision making.
Secure Cloud Applications
Secure, scalable cloud-based applications deliver role-based insights and controlled access across utility teams.
Data Foundations
A governed, scalable foundation with quality controls, metadata, and lineage tracking improves risk insight, ensures traceability, and produces consistent, regulator-ready reporting.
Responder Portal
Provide responders with secure access to infrastructure maps and safety information to support situational awareness, emergency response, training and cross-agency coordination.
Activation and storm planning
Evaluate conditions, model thresholds, and map asset risk to inform PSPS decisions. Built-in reporting ensure actions are defensible and customer impacts are clearly assessed.
Automated Customer Outage Communication
Automated SMS, email, voice, and portal alerts keep customers informed of outages, PSPS, and restoration to meet regulatory requirements while improving transparency.
PSPS Decision Tool
Evaluate conditions, model thresholds, and map asset risk to inform PSPS decisions based on risk and current conditions. Built-in reporting ensure actions are defensible and customer impacts are clearly assessed.
Risk modeling solutions
Leverage Risk-Spend Efficiency and Cost-Benefit Analysis to prioritize investments in risk reduction for wildfire mitigation and increased reliability
Optimize inspection and maintenance processes
Define high risk zones for enhanced vegetation and asset management and optimize inspection scheduling to reduce truck rolls and risk.

We will never sell your data. View our privacy policy here.
What is risk management in the utilities sector?
Utility risk management is the structured process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats that could disrupt operations, endanger public safety, or strain financial resources. These risks come from environmental hazards, regulatory pressures, infrastructure challenges, and financial constraints. By adopting a structured risk management approach, utilities can prevent disruptions, strengthen resilience, and meet evolving regulatory requirements.
The risks utilities face are diverse and evolving:
Environmental risks
Wildfires, extreme weather, and other climate change–related events
Operational risks
Equipment failures, vegetation overgrowth, and aging assets that increase the likelihood of outages
Regulatory risks
Complex, evolving compliance requirements from federal, state, and local agencies
Financial risks
Budget constraints, cost recovery challenges, and investment decisions that impact long-term stability
Taking a holistic approach to risk management is essential for long-term success. Instead of addressing risks in isolation, utilities must integrate data-driven insights, cross-departmental collaboration, and proactive planning to develop a comprehensive strategy. A well-rounded approach considers not only immediate threats, but also long-term resilience, ensuring that risk mitigation efforts align with broader operational, regulatory, and financial goals.
Advanced risk modeling, predictive analytics, and modernized infrastructure allow utilities to transition from reactive to proactive risk management, improving resilience, resource allocation, and decision making.
Learn more about how utilities are addressing specific sources of risk:
Vegetation management
- Schedule optimization
- Risk zone mapping
- Enhanced vegetation management for wildfire mitigation
- Image data strategy and analysis—LiDAR, satellite, drone
Wildfire mitigation
- Utility Digital foundations including Digital Twin
- Grid investment planning including Risk-spend efficiency (RSE) calculations and cost-benefit analysis
- Risk informed maintenance
Asset management analytics
- Computer vision for maintenance and inspection
- Asset health monitoring
- Remote inspection
Emergency preparedness
- Resiliency infrastructure and application modernization
- Event simulation and training
- PSPS decision tools
- Automated customer notification

Case study
Data-driven risk mitigation in action
A major California utility partnered with Logic20/20 to enhance wildfire prevention using AI-driven risk mitigation. Traditionally, inspections were manual and inconsistent, delaying issue detection. To improve efficiency, the utility deployed an AI-powered inspection system that analyzed drone imagery to identify equipment anomalies with up to 80% accuracy. This data-driven approach accelerated maintenance decisions, strengthened safety, and improved compliance.
A holistic approach to managing utility risk
Utilities face growing risks from climate change, aging infrastructure, and evolving regulations. Meeting these challenges requires a holistic, data-driven approach that strengthens resilience, enhances situational awareness, and supports compliance. By combining strong data foundations, advanced risk models, and secure applications with proven operational tools, utilities can make better decisions and reduce risk across the grid.
Building strong data foundations
We help utilities establish the data foundations that make holistic risk management possible. Structured data and adaptable workflows are essential for modern utility risk management, enabling better decision-making and coordination across teams. By integrating asset, vegetation, geospatial, weather, and risk data into a unified environment, utilities can gain a full view of vulnerabilities and prioritize investment. Our data governance practices ensure data quality, ownership, and update processes across both operational and analytical systems.
Digital twins for scenario planning
Digital twins offer a dynamic, virtual representation of circuits and critical assets. By integrating inspection data, load forecasts, and operating states, utilities can simulate risk scenarios, compare mitigation tactics, and prioritize projects based on risk-spend efficiency.
Secure cloud applications
Cloud-based applications deliver secure, scalable, role-based insights across utility teams. With features like scenario planning, risk visualization, and controlled access, utilities can enhance situational awareness, coordinate response strategies, and maintain compliance under regulatory scrutiny.
AI-powered risk models
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming how utilities identify and mitigate risk. By analyzing climate patterns, inspection images, sensor data, and historical failures, our predictive models can estimate asset degradation, vegetation risk, and wildfire likelihood. These insights help utilities focus inspections, extend asset life cycles, and guide proactive investments in grid hardening.
RSE modeling: Evaluating cost-benefit tradeoffs
Risk-Spend Efficiency (RSE) modeling helps utilities evaluate risk mitigation strategies by comparing potential risk reduction against investment costs. This approach enables providers to balance priorities such as grid hardening, vegetation management, and infrastructure upgrades while maximizing operational and financial efficiency. A structured RSE model supports long-term resilience by ensuring that resources are allocated where they have the greatest impact.
> Read more about Refining risk management with risk-spend efficiency (RSE)
Proven tools for operational resilience
Physical tools such as grid hardening and sensors are critical to building resilience, but deploying them effectively requires knowing where they will have the most impact. Our AI-powered risk models help utilities evaluate and prioritize investments in these tools by predicting where they will deliver the greatest risk reduction.
- Grid hardening and infrastructure upgrades — including fire-resistant insulator caps, undergrounding, and advanced circuit breakers.
- Weather stations to capture hyperlocal, real-time conditions that improve situational awareness.
- Enhanced powerline safety settings (EPSS) that minimize ignition risk during high-fire conditions.
- Advanced sensors that monitor pole tilt, asset degradation, or ignition events before they escalate.
With data-driven insights, utilities can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that resilience measures target the highest-risk areas
Insights

How AI is transforming utility emergency operations
How Gen AI is transforming utility emergency operations, as evidenced by a proof-of-concept AI decisioning assistant built by our team

Optimizing vegetation management: Advanced strategies
How AI, machine learning, and data integration are transforming vegetation management to enhance safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance

AI desktop inspection: Transforming asset management
How AI-powered desktop inspections enhance asset management and predictive maintenance using drones and computer vision.
What are your risk management challenges? Let’s talk through the solutions.

Climate change and related risks for power and utilities
Utilities must navigate an increasingly unpredictable operating environment, where extreme weather raises the risk for emergency situations and accelerated deterioration of infrastructure assets. Effectively managing these risks requires breaking down data silos, improving real-time monitoring, and coordinating across departments to implement scalable mitigation strategies.
Identifying climate risks
Recent data from NASA indicates that human activities have raised the atmosphere’s carbon dioxide content by 50 percent in less than 200 years, contributing significantly to global warming.
As climate change accelerates, utilities face increasing challenges from environmental hazards that can disrupt operations and threaten public safety. Identifying these climate risks is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and ensuring long-term resilience.
Key climate risks include:
- Extreme weather events: Increased frequency and severity of storms, heatwaves, and heavy precipitation can damage infrastructure and lead to service interruptions.
- Sea-level rise and flooding: Coastal utilities may experience infrastructure damage due to rising sea levels and increased flooding, impacting service reliability.
- Wildfires: Prolonged droughts and higher temperatures elevate wildfire risks, particularly in areas with extensive vegetation near power lines.
- Environmental regulatory and policy changes: Evolving environmental regulations require utilities to adapt operations to meet new compliance standards.
Climate risks and extreme weather
Extreme weather events are becoming less predictable and more severe, making traditional risk management approaches less effective. Utilities must adopt predictive climate modeling, scenario planning, and adaptive infrastructure strategies to mitigate risks effectively. By integrating real-time data analysis, historical weather tracking, and AI-driven analytics, utilities can improve response times, strengthen grid resilience, and reduce operational disruptions. Long-term climate projections help utilities prioritize investments that strengthen infrastructure against evolving risks.
Infrastructure investments and operational risks
Managing vast networks of aging infrastructure requires strategic decision making. Utilities must determine which assets to upgrade or replace first, optimize vegetation management programs, and deploy cost-effective solutions that enhance grid reliability without unnecessary spending. Without data-driven prioritization, utilities risk inefficient spending and increased system failures.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is an example of risk mitigation?
One example of risk mitigation is how a major California utility leveraged AI-driven inspections to reduce wildfire risk. Traditionally, the utility relied on manual, on-site inspections to identify equipment issues—an approach that was time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies. To improve efficiency and safety, the utility deployed an AI-powered inspection system that analyzed drone imagery to detect equipment anomalies with up to 80% accuracy.
This data-driven risk mitigation strategy allowed the utility to:
- Prioritize high-risk areas for maintenance, reducing wildfire threats
- Reduce manual inspections, lowering operational costs
- Enhance compliance tracking, ensuring alignment with regulatory requirements
By integrating AI and predictive analytics, the utility successfully transitioned from reactive to proactive risk management, improving both safety and operational efficiency.
What are some risk management strategies for utility companies?
Utility companies use proactive, data-driven strategies to mitigate risks and ensure long-term resilience. Key strategies include:
- Advanced risk modeling: AI and predictive analytics help utilities forecast wildfire threats, asset failures, and extreme weather impacts, allowing for targeted risk mitigation.
- Data-driven risk mitigation: Real-time data analytics, remote sensing, and predictive risk scoring enable utilities to prioritize vegetation management, streamline maintenance scheduling, and refine emergency response plans.
- Grid hardening and infrastructure upgrades: Investments in fire-resistant materials, underground power lines, and automated grid controls help utilities withstand severe weather and external threats.
- Risk-Spend Efficiency (RSE) modeling: By evaluating risk reduction versus cost, utilities can allocate resources efficiently, balancing investments in grid resilience, vegetation management, and asset modernization.
- Cloud-based risk platforms and digital twins: These tools centralize risk data, support real-time monitoring and compliance tracking, and allow utilities to simulate failure scenarios to refine mitigation strategies before implementation.
By integrating these strategies, utilities can transition from reactive to proactive risk management, improving safety, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Why is risk management important for utilities?
Effective risk management helps utilities protect infrastructure, maintain reliable service, and comply with regulatory requirements. Without a structured approach, utilities face increased operational costs, safety hazards, and regulatory penalties.
Key benefits of risk management include:
- Enhancing public safety: Prevents wildfires, power outages, and infrastructure failures that could endanger communities.
- Improving regulatory compliance: Ensures adherence to mandates from agencies like FERC and NERC, reducing the risk of fines and legal challenges.
- Optimizing resource allocation: Risk-Spend Efficiency (RSE) modeling helps utilities prioritize investments in grid hardening, vegetation management, and asset upgrades.
- Reducing financial risk: Identifies and mitigates costly disruptions, preventing unexpected repair expenses and revenue losses.
Increasing operational resilience: Enables utilities to anticipate and respond to extreme weather, cyber threats, and equipment failures before they escalate.
By implementing data-driven risk management strategies, utilities can ensure long-term reliability, regulatory alignment, and financial stability in an increasingly complex environment.
What are some utility risk mitigation tools?
Utility companies use a combination of advanced technologies and analytical tools to identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively. Key risk mitigation tools include:
- AI-driven risk modeling: Uses machine learning to predict asset failures, wildfire risks, and extreme weather impacts, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Digital twins: Creates real-time simulations of grid infrastructure and failure scenarios, allowing utilities to test and refine mitigation strategies before implementation.
- Cloud-based risk platforms: Centralizes risk data, compliance tracking, and emergency response coordination, improving decision-making and disaster recovery.
- Geospatial and remote sensing tools: Use satellite imagery, LiDAR, and drones to monitor vegetation growth and infrastructure vulnerabilities.
- Predictive maintenance systems: Leverage sensor data and analytics to detect early signs of equipment degradation, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
- Risk-Spend Efficiency (RSE) modeling: Helps utilities quantify risk reduction vs. cost, ensuring that mitigation investments maximize safety and financial sustainability.
By integrating these data-driven risk mitigation tools, utilities can enhance safety, improve resilience, and optimize operational efficiency.
What are the key steps in utility risk mitigation?
Effective utility risk mitigation follows a structured approach to identify, assess, and address potential threats. Key steps include:
- Identifying risks: Use historical data, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics to assess vulnerabilities, such as extreme weather, asset failures, and vegetation overgrowth.
- Evaluating impact: Conduct risk assessments and scenario modeling to quantify potential financial, operational, and regulatory consequences.
- Developing mitigation strategies: Implement AI-driven risk modeling, grid hardening, vegetation management, and asset upgrades to reduce risks effectively.
- Prioritizing risk reduction efforts: Use Risk-Spend Efficiency (RSE) modeling to allocate resources where they provide the greatest impact at the lowest cost.
- Monitoring and adjusting strategies: Continuously track risk trends, compliance changes, and mitigation effectiveness using cloud-based risk platforms and digital twins.
By following these steps, utilities can transition from reactive to proactive risk management, ensuring long-term reliability, compliance, and financial stability.
