5-minute read
By now the benefits of intelligent process automation are well known, and thanks to the availability of cost-efficient, user-friendly automation software, more organizations are reaping the rewards. These benefits are often realized through the use of a comprehensive automation platform that integrates AI, robotic process automation (RPA), and low-code process automation (LPA) to streamline complex business processes. By 2026, according to a recent study by Gartner, 30 percent of enterprises will have automated more than half of their network activities, an increase from under 10 percent in 2023.
As this trend accelerates, the future of automation has begun to take shape, and that future is intelligent. Many organizations are bumping up against the limitations of traditional automation and recognizing the need for a solution that goes beyond rule-based algorithms. By blending automation and AI, organizations can evolve their processes to the realm of intelligent process automation, uncovering opportunities to make their processes even more efficient, less error-prone, and less reliant on human intervention.
What is intelligent process automation?
Traditional automation is, for lack of a better word, “dumb,” in that it relies on rules that human knowledge workers have programmed into it (“if this, then that”). If an automated system comes across a scenario for which it has no rule in its programming, or if the data it receives is incomplete or irregularly formatted, it cannot move forward and humans must intervene. That’s why traditional automation is well-suited for simple, rule-based tasks with few exceptions, but fall short when it comes to more complex processes.
With intelligent process automation, systems become more autonomous, requiring less human input. AI and related technologies—including machine learning, natural language processing, speech recognition, and computer vision—enter the picture to allow automation to go beyond the limits of rules-based programming. Whereas traditional automation systems “learn” by being manually programmed, intelligent process automation learns by continuous observation.
In today’s IT and business environments, it is crucial for automation platforms to integrate seamlessly with various systems and technologies to manage data effectively.
To look at intelligent process automation another way, think of the AI component as “the brain” that’s in charge of learning, applying learned knowledge, and supervising the process. Technologies such as computer vision and speech recognition are “the eyes and ears,” tasked with taking in data and translating it into usable formats. And the automation systems are “the hands” that execute the prescribed tasks as directed by the AI component.
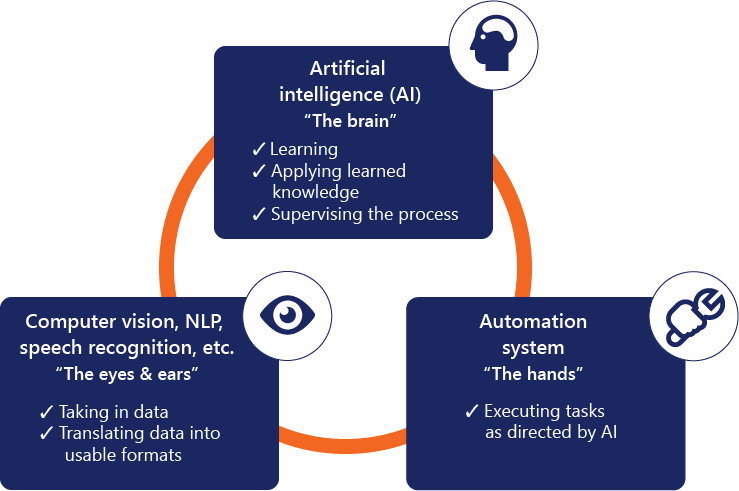
Key components of intelligent process automation
Intelligent process automation integrates several advanced technologies to enhance and streamline business operations. Below is a breakdown of some of its essential components:
- Robotic process automation: Automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human actions, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing errors. By combining RPA with AI and analytics, organizations can create dynamic and adaptable operational models that respond to changing market conditions
- Smart workflow: Manages and optimizes the flow of tasks and information across processes, ensuring seamless coordination and improved productivity
- Advanced analytics: Utilizes data analysis techniques to provide insights, enabling informed decision making and identifying opportunities for process improvements
- Natural language processing (NLP): Allows systems to understand and interpret human language, facilitating better interaction between humans and machines
- Cognitive agents: AI-powered virtual assistants capable of performing tasks, learning from interactions, and adapting to new information to provide personalized support
Intelligent process automation vs robotic process automation
While intelligent process automation and robotic process automation are related technologies, they differ in scope and capabilities. RPA is a foundational element of IPA, focusing on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. In contrast, IPA builds upon RPA by incorporating advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and natural language processing to handle more complex and dynamic processes.
It is also important to calculate the ROI of these technologies by comparing the costs associated with implementing automation solutions against the costs of manual processes.
RPA delivers significant value to businesses by automating tasks and workflows. Key benefits include:
- Increased efficiency: Automates high-volume tasks, reducing processing times and freeing up employees for higher-value activities
- Cost savings: Reduces operational costs by minimizing manual labor and improving process consistency
- Error reduction: Ensures greater accuracy by eliminating human error in repetitive tasks
- Improved compliance: Provides audit trails and ensures adherence to regulatory standards by automating processes with strict rules
- Scalability: Adapts easily to changing business demands, enabling organizations to scale operations without significant overhead
By understanding the distinctions and synergies between RPA and IPA, businesses can strategically leverage both technologies to optimize processes, improve decision making, and drive innovation.
Business process management and automation
Business process management (BPM) is a cornerstone of intelligent automation, enabling organizations to streamline and optimize their processes. By combining robotic process automation with BPM, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, significantly reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency. BPM involves identifying, analyzing, and optimizing business processes to achieve better outcomes. With intelligent automation, BPM can be elevated to a new level, allowing organizations to enact changes swiftly and efficiently. This integration not only improves process efficiency, but also ensures that businesses can adapt to evolving market conditions with agility.
Use case: traditional vs. intelligent process automation in financial services
One area where intelligent process automation is making an impact is in the financial services industry, particularly in call centers. A bank’s customer service representatives spend as much as 75 percent of their time doing manual research, including looking up offers for each caller in real time.
Intelligent automation enables bots to quickly answer customer inquiries, thereby enhancing efficiency in customer service departments.
With traditional automation, an agent’s screen may show offers based on the customer’s geographic location or current promotions. AI and machine learning enable digital workers to search the caller’s account, combine that data with information being gathered on the call in real time, and send a predicted “next best offer” to the agent’s screen, tailored to the specific customer. This streamlined process results in
- Shorter call times: Agents have instant access to the information they need to pass on to the customer—no awkward silences while they scroll through the available offers.
- Improved customer satisfaction: More personalized offers help customers feel valued and appreciated.
- Higher conversion rates: Customers are more likely to accept offers tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
How it works
The following graphic shows how a process can evolve from a purely manual approach to traditional automation to intelligent process automation, and how each layer adds capabilities that save time and effort, reduce the risk of error, and improve overall efficiency:
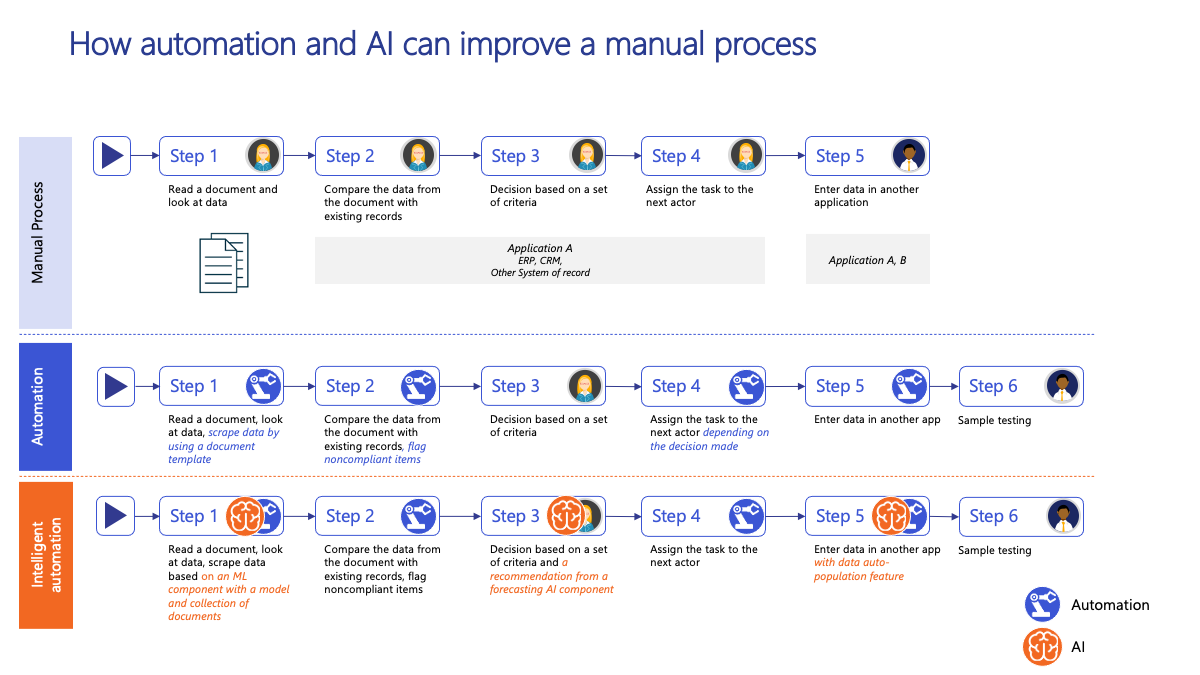
Benefits of intelligent process automation
You may notice a striking similarity between the benefits of intelligent process automation and the benefits of traditional automation, and rightly so. The primary benefit of intelligent process automation is that it allows automation to do what it already does—only better, faster, and with less intervention from human employees. With intelligent process automation, organizations can deploy automated processes and workflows quickly and efficiently, enhancing operational efficiency.
Heightened efficiency
Intelligent process automation eliminates many of the “speed bumps” that arise from the need for human intervention, allowing processes to execute more smoothly and efficiently. As intelligent automation systems continue to innovate, they transform operations and drive business growth.
Less programming
Because intelligent process automation learns on its own, the organization reduces the need to devote resources to programming—and re-programming—its automation rules.
Higher employee satisfaction
The addition of AI reduces the number of instances that require manual intervention, enabling human workers to spend less time supervising automated processes and more time doing engaging, satisfying work.
Better customer experiences
Intelligent process automation enables businesses to create more personalized customer experiences based on the sum total of past interactions rather than on rule-based algorithms, which can improve customer satisfaction and retention rates. Predictive analytics can generate insights from data collection, helping businesses understand customer intent and enhance customer experiences.
Improved regulatory oversight
While traditional automation relies on pre-programmed rules in monitoring transactions and processes for potential compliance violations, intelligent process automation looks for patterns in the data and refers to a domain knowledge base to determine whether those patterns indicate a compliance risk. Human workers only need to enter the picture when a new pattern is discovered, and the results of the intervention feed back into the domain knowledge base to serve as a reference for future cases.
Reduced overall costs
Intelligent process automation streamlines operations by automating repetitive tasks, optimizing workflows, and reducing dependency on manual labor. This approach minimizes operational inefficiencies, such as delays and errors, which can incur additional costs. By leveraging technologies like advanced analytics and cognitive agents, IPA also enables more accurate decision making and better resource allocation, further driving down expenses. Over time, these efficiencies contribute to significant cost savings, allowing organizations to reinvest in growth and innovation.
Driving efficiency and satisfaction with intelligent process automation
Intelligent process automation helps businesses streamline operations, automate tasks, and improve customer satisfaction. In manufacturing, IPA reduces errors and accelerates production by handling repetitive processes like data entry. In customer service, it enables faster, more accurate responses, boosting efficiency and elevating the customer experience. Financial institutions use IPA to monitor transactions and ensure compliance more effectively. With built-in analytics, IPA supports smarter decision making, empowering digital transformation across industries.
Optimize workflows and unlock data insights
Automating workflows with IPA eliminates manual bottlenecks and accelerates business processes. At the same time, IPA automates data collection and analysis, revealing insights that drive operational efficiency and continuous improvement. This dual capability strengthens performance while supporting data-driven strategies.
Reimagining HR through digital transformation
HR teams are central to any digital transformation initiative. With IPA, they can automate tasks like recruiting and onboarding, allowing more focus on strategic workforce planning. Predictive analytics further enhances decision making, helping HR anticipate needs and support future growth more effectively.
How to implement intelligent process automation in your organization
Adopting intelligent process automation (IPA) can transform the way your organization operates, delivering benefits such as increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and reduced costs. To realize these advantages, it’s important to take a structured approach to IPA implementation. Below are key steps to guide business leaders as they incorporate IPA into their organizations:
Align processes with IPA implementation
Start by identifying processes that are repetitive, time-consuming, and prone to human error. These are ideal candidates for automation and can provide immediate benefits. Additionally, align IPA initiatives with your broader business objectives to ensure that automation supports key priorities, such as improving customer experiences or reducing operational bottlenecks.
Build an effective strategy
A well-rounded strategy is critical to the success of your IPA implementation. This includes selecting the right processes for automation, choosing technologies that integrate seamlessly with existing systems, and preparing your organization for change. To avoid common pitfalls, prioritize clear communication with stakeholders, focus on measurable outcomes, and ensure alignment across teams.
Grab quick wins
Pilot projects are an excellent way to demonstrate the value of IPA while identifying opportunities for improvement. Target processes with clear outcomes that can deliver quick wins, such as reducing task completion times or cutting costs. Use these early successes to build momentum, refine your approach, and scale automation efforts to drive long-term transformation.
Establish a Center of Excellence (CoE)
Creating a Center of Excellence (CoE) ensures your IPA initiatives are well-managed and sustainable. A CoE provides systematic oversight, promotes best practices, and embeds digital capabilities into your organization’s operations. By fostering business ownership and integrating IPA skills within teams, a CoE supports ongoing innovation and helps maintain the long-term success of your automation efforts.
The future of intelligent process automation
Businesses across industries have realized the benefits of automation, and they’re ready to take the next step. By applying artificial intelligence to enable intelligent process automation, organizations can begin creating a true digital workforce capable of simulating many aspects of human thought and judgment. When this happens, the initial promises of automation—faster processes, lower costs, lower risk of error, freeing employees from the most repetitive tasks—can rise to a new level, delivering even greater benefits to the bottom line.

Claim your competitive advantage
We create powerful custom tools, optimize packaged software, and provide trusted guidance to enable your teams and deliver business value that lasts.