12-minute read
Quick summary: Five key digital transformation trends that will be shaping businesses in 2025
With 2025 nearly upon us, the pace of technological innovation shows no signs of slowing. To thrive in this era of rapid change, organizations are embracing advancements in AI, modernizing their operational infrastructure, and preparing for transformative shifts. Trends like agentic AI, resilient systems, and hyper-personalized customer experiences are not just reshaping industries—they’re redefining the rules of competition.
In this article, we’ll explore the most impactful technology trends poised to shape the year ahead, highlighting not only the opportunities created by innovation, but also the challenges of governance, adaptability, and staying resilient in a fast-changing digital landscape. Drawing on real-world examples and expert insights, we offer actionable takeaways to help businesses navigate these shifts and prepare for a future dominated by AI-driven decision making, cloud-powered operations, and seamless customer engagement.
Article continues below.
WEBINAR
Decoding AI complexity: A leader’s guide to generative AI in the enterprise
Trend #1: Agentic AI: Reshaping innovation through accessibility
As AI becomes more integral to business strategies, its adoption is no longer confined to highly technical teams. Agentic AI, a concept that goes beyond the often-cited “democratization of AI,” is transforming how organizations innovate by making artificial intelligence more accessible, actionable, and effective for a broader range of users.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to the evolution of AI tools, enabling non-technical users to deploy and leverage AI-driven solutions. Platforms like Microsoft Copilot Studio, OpenAI’s GPTs, and Amazon Q exemplify this trend by offering low-code or no-code environments. These tools allow users across organizations—from project teams to HR departments—to build bots, automate workflows, and analyze data without requiring extensive expertise in machine learning or data science.
Key drivers behind agentic AI
- The low-code/no-code revolution: The rise of intuitive platforms has significantly reduced barriers to entry for AI adoption, empowering professionals in every department to experiment with AI-driven processes.
- Ease of implementation: By providing prepackaged solutions, agentic AI tools eliminate the complexity traditionally associated with AI development, making it easier and faster to deploy impactful applications.
Opportunities for businesses
Agentic AI accelerates innovation by putting powerful tools into the hands of diverse teams across an organization. Beyond individual use cases, businesses can scale these capabilities to an enterprise level, creating a more cohesive and efficient AI ecosystem. For example:
- Tailoring interactions to drive engagement: Marketing teams can create AI agents that tailor interactions to individual preferences, driving higher engagement and conversions.
- Transforming content into accessible formats: AI agents can automatically process and transform complex or unstructured content into accessible formats, making it easier to find, understand, and consume. This capability supports better knowledge management and accessibility across the organization.
- Scaling through enterprise AI agents: Organizations can implement a hierarchical structure of AI agents, where higher-level agents oversee and coordinate the activities of lower-level agents. This approach fosters efficient task delegation, streamlined knowledge sharing, and cohesive decision making, driving innovation at scale.
Challenges to consider
Alongside its many promises, agentic AI also introduces new challenges:
- Governance gaps: As AI tools become easier to use, ensuring data ethics and security can become more complex. Many organizations have established a “value realization office” or similar framework to assess whether AI projects align with corporate goals and deliver measurable value.
- Illusion of simplicity: Many tasks seem deceptively simple with agentic AI. However, the quality of the output is often directly tied to the quality of the input data and the context provided. Moreover, the effectiveness of these agents depends on how well they evolve over time to address changing needs and complexities. Businesses can seize this opportunity to build enterprise-level solutions that support both lines of business and IT departments, ensuring robust and adaptable systems.
The future of agentic AI
Looking ahead, agentic AI is poised to become a cornerstone of digital transformation. Gartner predicts that by 2028, 15 percent of day-to-day workplace decisions will be made autonomously by AI. For organizations, this underscores the importance of flexibility and continuous innovation.
Trend #2: Building resilient applications for critical operations: Ensuring uptime in a volatile world
As organizations grow increasingly reliant on digital systems to drive operations, the demand for resilience in critical applications has never been higher. Ensuring continuous uptime is essential for maintaining customer trust, protecting data, and sustaining business operations, whether in utility control centers or in financial services platforms.
Recent high-profile outages, such as the July 2024 disruptions experienced by Microsoft and AWS, have highlighted the significant risks tied to cloud dependency. These incidents affected a wide range of businesses, exposing vulnerabilities in critical systems that lacked robust resiliency planning. Organizations that fail to prioritize resiliency in their critical applications face increased risks of operational disruptions, financial losses, and reputational harm.
To address these challenges, businesses must design application architectures that incorporate redundancy, scalability, and proactive monitoring. By planning for resilience and preparing for potential cloud disruptions, organizations can ensure continuous operation and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders.
Why resilience matters
Modern IT ecosystems are interconnected, complex, and vulnerable to a wide array of disruptions. Organizations depend on critical applications to handle real-time customer interactions, manage operational workflows, and deliver essential services. Without proper resilience strategies in place, major disruptions can arise, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and customer dissatisfaction.
Core components of resilient functions
- Cloud-native architectures: Cloud-based solutions offer inherent scalability, flexibility, and built-in redundancy. These features ensure that applications can handle fluctuating workloads and recover quickly from unexpected disruptions.
- Microservices: By breaking down applications into smaller, independent components, organizations can isolate faults and improve recovery times. This modular approach also simplifies updates and scaling.
- AI-driven automation: AI can monitor systems, detect anomalies, and automate incident responses, reducing downtime and accelerating recovery processes.
- Continuous testing and monitoring: Regular testing and real-time monitoring help identify vulnerabilities and address issues proactively before they escalate into major outages.
The risks organizations face
Building resilience means preparing for a range of threats, including:
- Cyberattacks: Malicious actors targeting critical systems can cause data breaches, financial losses, and prolonged downtime.
- Natural disasters: Events like hurricanes, earthquakes, wildfires, and floods can disrupt infrastructure and impede recovery efforts.
- Human error: Accidental misconfigurations or mistakes can compromise system availability and data integrity.
- Supply chain disruptions: Shortages of critical components or third-party service failures can cascade into operational challenges.
Goals of a resilient application strategy
To mitigate these risks, organizations are prioritizing system resilience by:
- Minimizing downtime: Ensuring critical systems remain operational, even in the face of disruptions
- Protecting critical assets: Safeguarding sensitive data, intellectual property, and operational resources
- Enhancing reputation: Delivering reliable services that maintain customer trust and loyalty
- Achieving regulatory compliance: Meeting standards like the FERC CIP for utilities, which mandates safeguards for the bulk electric system to ensure its reliability and security
- Gaining a competitive edge: Delivering uninterrupted, high-quality services to gain an edge over competitors
The role of energy-efficient computing
Resilient systems can also align with sustainability goals through energy-efficient computing. By optimizing power consumption and leveraging greener technologies, organizations can reduce their carbon footprint while ensuring operational integrity.
The future of resilience in critical operations
In an era where downtime is no longer acceptable, resilience is more than a technical feature—it’s a business imperative. Organizations are investing in resilient architectures that combine cloud capabilities, automation, and proactive monitoring to stay ahead of threats and disruptions.
Modern IT ecosystems are interconnected, complex, and vulnerable to a wide array of disruptions. Without proper resilience strategies in place, major disruptions can arise, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and customer dissatisfaction.
Trend #3: Hyper-personalized and invisible customer experiences: Redefining how brands engage
Customer expectations are evolving rapidly, driven by the convergence of advanced technologies like agentic AI, natural language processing, and ambient invisible intelligence. These innovations are enabling hyper-personalized, seamless interactions that are redefining how brands connect with their audiences. Customers now expect intuitive, proactive experiences that anticipate their needs—often before those needs are explicitly stated.
The rise of invisible intelligence
Invisible intelligence refers to systems that work behind the scenes to deliver proactive solutions without requiring active input from users. For example, smart home systems are adjusting lighting and temperature based on user preferences and habits, while AI-driven apps are preemptively suggesting services or products tailored to individual lifestyles. This shift is transforming customer experiences by making them more seamless and removing friction.
Key shifts in customer interactions
- Natural language interfaces: Voice assistants and chatbots are increasingly replacing traditional menus and forms. These conversational AI systems provide users with human-like interactions, enabling more efficient and engaging exchanges.
- Hyper-personalization: Analyzing vast amounts of data enables brands to deliver highly targeted marketing messages, product recommendations, and user experiences that feel tailored to each individual.
- Agentic AI companions: AI-powered virtual assistants are evolving into empathetic companions capable of understanding and responding to complex emotions, further enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
The new customer contract
This trend of hyper-personalization and invisible intelligence comes with a tradeoff: Customers are willing to share personal data but expect value, transparency, and ethical practices in return. To meet this expectation, companies are:
- Investing in AI infrastructure: Organizations are building robust data pipelines and leveraging AI to process and act on customer insights effectively.
- Prioritizing user experience (UX): Seamless, intuitive design is becoming a critical differentiator, ensuring that customers feel supported and understood at every touchpoint.
- Fostering trust through transparency: Clear communication about how customer data is used helps brands build lasting relationships.
- Embracing ethical AI: Companies are aligning their AI systems with societal values to mitigate bias and protect customer privacy.
Business implications
The shift toward hyper-personalized and invisible customer experiences is creating significant opportunities for businesses to:
- Forge deeper connections: Personalized interactions foster a sense of loyalty and trust, strengthening customer relationships.
- Drive engagement and retention: Tailored experiences encourage repeat business and long-term brand advocacy.
- Unlock new growth opportunities: Proactive insights and automation open the door to innovative products and services.
The future of customer experiences
The boundaries between technology and human interaction continue to blur. As brands adopt hyper-personalized and invisible intelligence–driven strategies, customer experiences will become increasingly intuitive and dynamic. Organizations that prioritize these innovations while safeguarding customer trust will gain a competitive edge in this new era of engagement.
Trend #4: Creating resilience through adaptable processes and empowered teams
In a “VUCA” world—marked by volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity—the only thing that is certain is change. Businesses and organizations need to be ready and able to respond quickly to change more now than ever before. However, most large businesses are doing business as they always have, creating a laundry list of risks that need to be constantly balanced (or not).
At a high level, businesses need to:
- Find processes and practices that work for the business and organization.
- Create a culture of resilience for employees in which teams are empowered, productive, and innovative.
- Create satisfied, happy customers who have their highest-impact needs addressed quickly and efficiently.
Organizations that can’t find the balance between process, culture, and customer value are at risk for:
- Missing business opportunities, as too much structure can make you slow to market, losing investment dollars in the process
- Loss of workers as they struggle to engage in and do the constantly changing work while also looking forward, innovating, and evolving alongside the technologies they work with
- Not finding the right balance between process and fluidity as poor or non-existent processes fail or don’t keep up with the pace of technological change
To mitigate the loss of business and employees and evolve alongside the pace at which technology evolves, organizations need to create better ways of working and build up a resilient workforce. Businesses can do the following:
- Build up processes and business practices capable of responding to constant change.
- Create a more resilient workforce through training, coaching, and mentoring.
- Create psychologically safe workspaces to allow better innovation.
- Build up leaders who are adept at dealing with change.
- Measure the things that matter to delivery and outcomes.
In a “VUCA” world—marked by volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity—businesses and organizations need to be ready and able to respond more quickly to change than ever before.
BONUS Trend #5: Modernizing OT with cloud adoption: Bridging the gap between IT and OT
The integration of operational technology (OT) into cloud ecosystems is gaining momentum, enabling organizations to modernize critical systems, enhance efficiency, and improve scalability. Once considered separate from traditional IT infrastructure, OT is now converging with cloud solutions to unlock new possibilities for resilience, innovation, and real-time operational insights.
The evolution of OT modernization
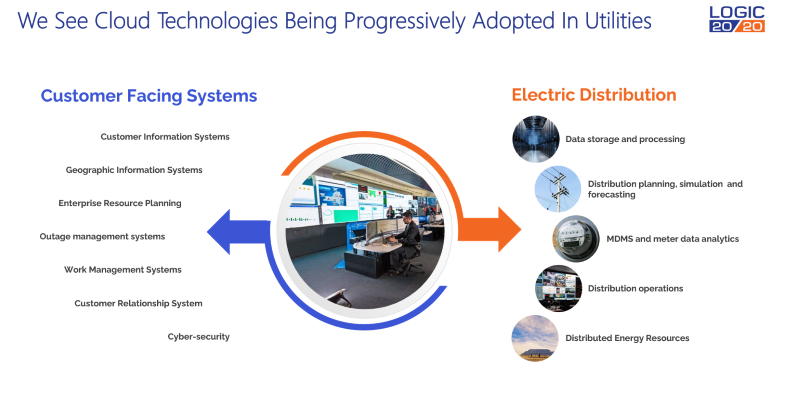
OT systems, such as those used for energy grids, industrial controls, and manufacturing processes, have historically operated in highly controlled and isolated environments. However, the increasing demand for swift data-driven decision making and operational efficiency has prompted industries to reimagine how OT systems are managed. Early adoption is evident in the utility industry, where cloud-enabled solutions like distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS) are paving the way for broader integration.
While the potential benefits of cloud-based solutions for utility advanced distribution management systems (ADMS) and other critical infrastructure applications are significant, current Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Critical Infrastructure Protection (FERC CIP) regulations pose notable limitations for U.S.-based utilities. These regulations, designed to ensure the security and reliability of the grid, often restrict the use of cloud-based technologies for critical systems.
As a result, many U.S. utilities are unable to fully leverage the advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Recognizing the potential benefits of cloud technology, many utilities are taking a proactive approach by experimenting with its implementation in DERMS, meter data management systems (MDMS), distribution planning, and operational systems. By doing this, utilities are positioning themselves for wider cloud adoption in operations.
However, solution providers in other parts of the world are actively testing and developing cloud-based ADMS, energy management systems (EMS), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. These efforts aim to demonstrate the feasibility and security of cloud technologies in the energy sector, paving the way for regulatory changes that could enable broader adoption in the future.
Use cases driving adoption
As the energy industry undergoes massive transformation, the cloud offers real opportunities for utilities to modernize the power grid, improve reliability and resiliency, and bring renewable energy projects online faster. According to Howard Gefen, General Manager for Energy and Utilities at AWS:
“Grid decentralization and decarbonization—driven by the integration of distributed renewable energy sources like solar and wind—are advancing quickly. Using the power and capabilities of the cloud in combination with grid orchestration software …, utilities can embrace emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and high-performance computing to innovate faster and balance the urgent need to decarbonize the grid and deliver more reliable and affordable energy to their customers.” (Source)
Key drivers behind cloud adoption include:
- Improved grid reliability and resilience: Cloud-based solutions empower utilities to better manage grid operations, optimize energy distribution, and rapidly respond to disruptions.
- Faster adoption of renewable energy projects: By leveraging high-performance computing and grid orchestration software, utilities can integrate distributed renewable energy sources like solar and wind more efficiently.
- Scalable innovation: The cloud enables utilities to adopt emerging technologies like IoT and advanced analytics, fostering faster development cycles and more effective solutions for grid modernization.
Overcoming challenges
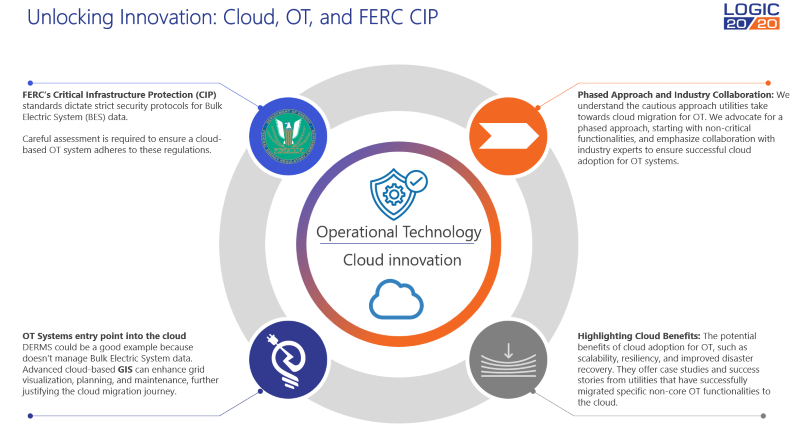
The journey to modernizing OT with cloud adoption is not without obstacles:
- Heightened compliance obligations: Utilities must adhere to stringent frameworks like the FERC CIP standards, which require robust safeguards for critical cyber assets.
- Slow pace of migration: Given the critical nature of OT systems, many organizations are taking a phased approach, starting with non-core functionalities to minimize risk and ensure smooth transitions.
A phased approach to OT cloud adoption
To address these challenges, organizations are adopting measured strategies:
- Start with low-risk systems: Prioritize migrating non-critical OT applications, such as monitoring tools or analytics dashboards, to gain early insights and build confidence in cloud capabilities.
- Collaborate with industry experts: Engage cloud providers and OT specialists to design architectures that align with regulatory requirements and business goals.
The benefits of cloud-enabled OT systems
For organizations willing to embrace cloud adoption, the benefits are transformative. Cloud-based solutions can adapt to changes in demand, enabling organizations to scale operations seamlessly. Cloud systems also offer redundancy and fast recovery capabilities, ensuring critical OT functions remain operational during disruptions. Finally, by transitioning legacy systems to the cloud, organizations gain access to advanced tools and technologies that drive efficiency and innovation.
The future of OT in the cloud
The convergence of OT and IT is no longer a distant goal—it’s a necessary step for organizations seeking to stay competitive in an increasingly interconnected world. Utilities and other industries are leading the charge, demonstrating how cloud adoption can unlock unprecedented levels of resilience, scalability, and insight. As more organizations embrace this trend, the boundaries between OT and IT will continue to blur, creating opportunities for smarter, more efficient operations.
Navigating the future: Embracing trends to lead in a digital-first world
The trends shaping digital transformation in 2025 share a common theme: Adaptability. Organizations are not just reacting to advancements in AI, cloud technologies, and customer engagement; they are leveraging these innovations to redefine how they operate and deliver value. By leveraging agentic AI to empower non-technical users and adopting hyper-personalized experiences to transform customer interactions, businesses are actively evolving to meet new demands and opportunities.
Resilience, personalization, and innovation are no longer optional—they are strategic imperatives. As organizations modernize their OT systems, build resilient applications, and adopt seamless, customer-centric technologies, they are future-proofing their operations. These shifts signal a cultural transformation toward experimentation, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
To stay ahead, businesses must embrace these trends and adopt a proactive mindset. This approach requires investing in technologies that enable flexibility, prioritizing governance to align innovation with ethical and business goals and fostering a culture that thrives on change. In doing so, organizations position themselves not just as participants in the digital-first future, but as leaders shaping its direction.
The path forward is clear: Those who embrace these trends with intention and agility will be best positioned to succeed in 2025 and beyond.

Claim your competitive advantage
We create powerful custom tools, optimize packaged software, and provide trusted guidance to enable your teams and deliver business value that lasts.


